Unit III Lesson 4
Annihilator Approach to
Method of Undetermined Coefficients
Annihilator operators, what they are what they do, the basic types. 
Proof by induction of one of the annihilator types. 
Find some annihilator operators for functions of various types. 
Outline of the technique for solving non-homogeneous equations using annihilator method. 
Example using the annihilator method for a non-homogeneous equation. 
Note that any nth order linear DE can be written with the differential
operator D:
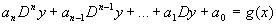 .
.
More simply, we could write L(y)=g(x) for
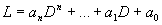 where L is a
linear operator.
where L is a
linear operator.
Recall also that operators can be factored.
Example:
(D2-5D+6)y=(D-3)(D-2)y

Def: Annihilator Operator
If L is a linear differential operator with constant coefficients and f is
a sufficiently differentiable function such that L(f(x))=0, then L is an
annihilator of f.

Examples of annihilators:
-
Dn annihilates 1,x,x2,…xn-1.
-
Dn also annihilates
c1+c2x+c3x2+…+cn-1xn-1
-
(D-A)n annihilates eAx, xeAx,
x2eAx, …, xn-1eAx
-
(D-A)n annihilates
C1eAx+C2xeAx+C3x2eAx+
…+ Cn-1xn-1eAx
-
(D2-2AD+(A2+B2))n annihilates
all of these:
eAxcos(Bx), eAxsin(Bx), xeAxcos(Bx),
xeAxsin(Bx), x2eAxcos(Bx),
x2eAxsin(Bx),…,xn-1eAxcos(Bx),
xn-1eAxsin(Bx)

Ex1. Show that (D-A)n annihilates
xn-1eAx by
induction.
Take this link after you've tried it yourself.
Here are some proof jokes if you are interested:
Methods
of proof
Weird humor link.
Ex2. Find an annihilator for each function:
-
f(x)=x4-7x2+2
-
f(x)=e2x
-
f(x)=4e2x-xe2x+x2e2x
-
(harder)
f(x)=9xe2xcos(3x)-5xe2xsin(3x) (hint: look at 5
above)
-
f(x)=Acos(kx)+Bsin(kx)
Take this link after you’ve tried these.
Technique for using annihilator method:
-
Find yc, the solution of the homogeneous equation L(y)=0
-
Operate on both sides of the non-homogeneous equation L(y)=g(x) with an
annihilator L1 that annihilates g(x).
-
Find the general solution of the higher order differential equation
L1(L(y))=0.
-
Delete from the solution of the equation all duplicates in yc,
and form a linear combination yp of the terms that remain. This
is the ‘form’ of the particular solution to L(y)=g(x). We need
the actual coefficients, so
-
Substitute this yp and its derivatives in the original equation
and solve for the coefficients, thus finding yp.
-
The solution is y=yc+yp

Ex3. (Hard!) Solve the differential
equation: y’’’+4y’=excos(2x)
Take this link after you've suffered for a while
yourself.
Comment: I don’t think any of the assigned problems are this tough!
Ex4. Annihilator problem.

****assignment****
Chapter 4 Section 5
Problems 1,7,13,15,17,21,23 (you don’t have to solve any of
these!)
35,49,53 (you do have to solve these), 69(IVP)





